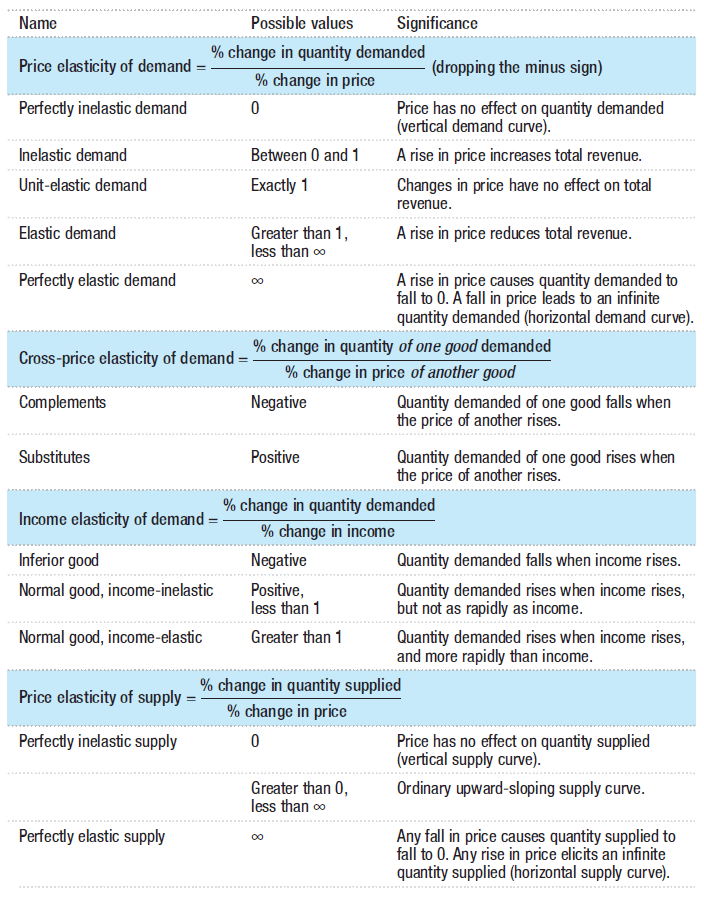
Cross-price elasticity of demand (EA,B)
Meaning
- Measure used to show the change in the price of one good affecs the demand for another good.
Formula
Percentage change in Quantity Demanded of Good A divided by Percentage change in Price of Good B
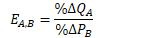
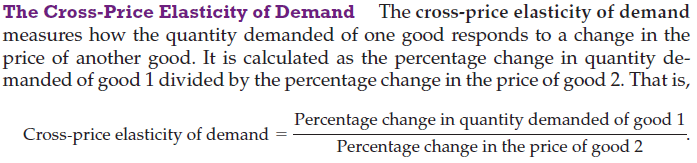
Substitutes
Definition
If the coefficient is positive, then the two items are substitutes.
*Do NOT find the absolute value for cross-price elasticity!
EA,B and substitutes
The higher the number, the more perfect the two items are as substitutes.
The lower the number, the less perfect the two items are as substitutes.
Price change and quantity demanded
If the price of Good A increases , then the quantity demanded of Good B will increase.
If the price of Good A decreases, then the quantity demanded of Good B will decrease.
Example

Complements
Definition
If the coefficient is negative, then the two items are complements.
*Do NOT find the absolute value for cross-price elasticity!
EA,B and substitutes
The more negative the number, the more perfect the two items are as complements.
The less negative the number, the less perfect the two items are as complements.
Price change and quantity demanded
If the price of Good A increases , then the quantity demanded of Good B will decrease.
If the price of Good A decreases, then the quantity demanded of Good B will increase.
Example
Income Elasticity of Demand
Meaning
- Measures how changes in income affect the demand for a good
Normal good vs. Inferior good
If the income elasticity of demand is positive, then it's a normal good.
If the income elasticity of demand is negative, then it's a inferior good.
Income-elastic vs. income-inelastic
If the income elasticity of demand is greater than 1, then it is income-elastic
If the income elasticity of demand is less than 1, then it is income-inelastic
Formula
Percentage change in Quantity Demanded Divided by Percentage change in Income
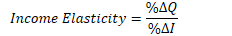
Example 1
- Income elastic good:
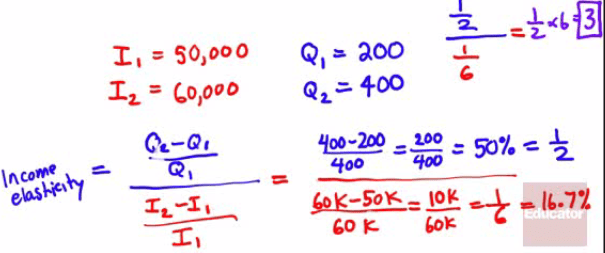
Example 2
- ceteris paribus: all other things being equal
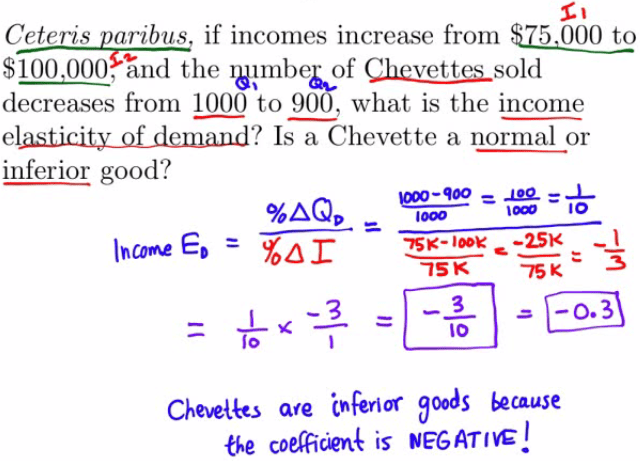
Example 3

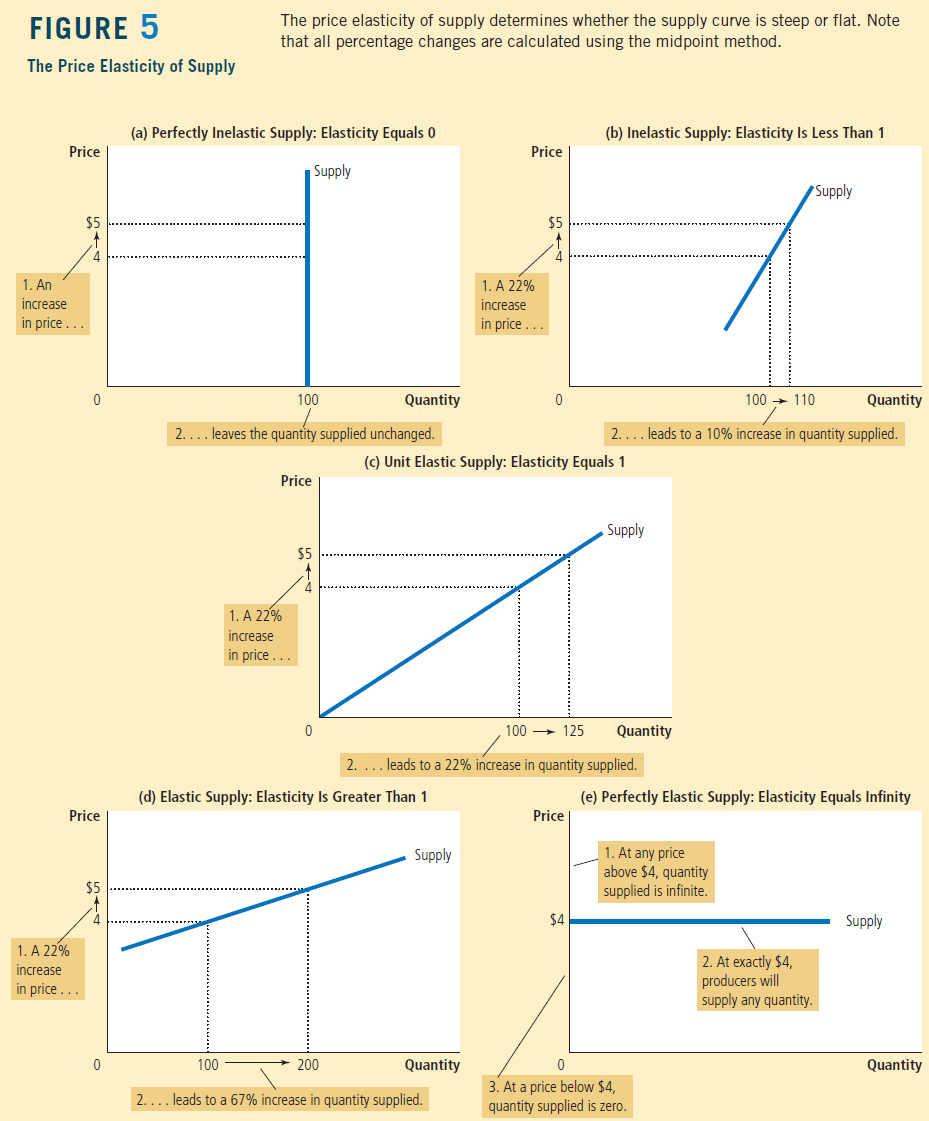
Price Elasticity of Supply
Meaning
- Measure of responsiveness of the quantity of a good supplied to the price of that good
Formula
Percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price

Availability of inputs affects elasticity
- Supply of pizza tends to be very elastic

Supply of cell phone frequencies is zero. The input (radio spectrum) cannot be changed

Graph
Summary for Elasticity